|
 |
|
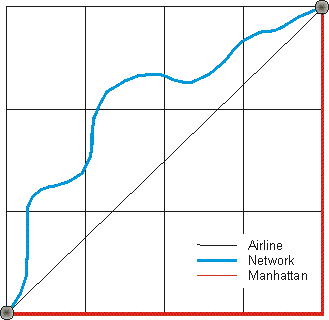
RRG GIS DatabaseInteraction data and regional data - Airline distances, network distances or Manhattan distancesThis type of interaction data provides distances between all pairs of a specific set of points of interest, using different approaches to measure the distance. Points of interest can be cities, centroids of statistical entities such as NUTS regions or administrative regions, railway stations, inland ports or seaports, motorway intersections or motorway exits, airports, hospitals, universities, mountain peaks or any other set of point locations or network elements. It is possible either to calculate distances between points of interest of the same type (e.g. between all pairs of capital cities), or between different points of interest (e.g. from all railway stations to all city centres). The distances are calculated using three different approaches:Airline distances represent the geographical distance between two points of interest, measured ‘as the crow flies’. Sometimes these distances are also referred to as ‘Euclidean distances’. Network distances represent the shortest path over the network between all points of interest. The networks considered can be road or rail networks or waterway networks, or any combination of these three modes. Manhattan distance is the length of the change in the x direction plus the change in the y direction of the coordinates of the points of interest considered, and is often used in urban contexts as an approximation of the network distance. For all the three methods, the distances will be measured in kilometres, metres, miles, feet, or inches. The network database used for the network distance calculation is the RRG GIS trans-European network database.
RRG GIS Database contents:General informationTransport networks Region boundaries, admninistrative boundaries Geography Interaction data and regional data Introduction |
|||||||||
|
|||||||||